Characterization of the aggressivity and erosivity of the rains in Ituporanga, Santa Catarina
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.52945/rac.v36i3.1766Keywords:
Precipitation, soil conservation, erosion, extreme eventsAbstract
Extreme rainfall is responsible for serious erosion problems and mass movements such as landslides. Rain erosivity
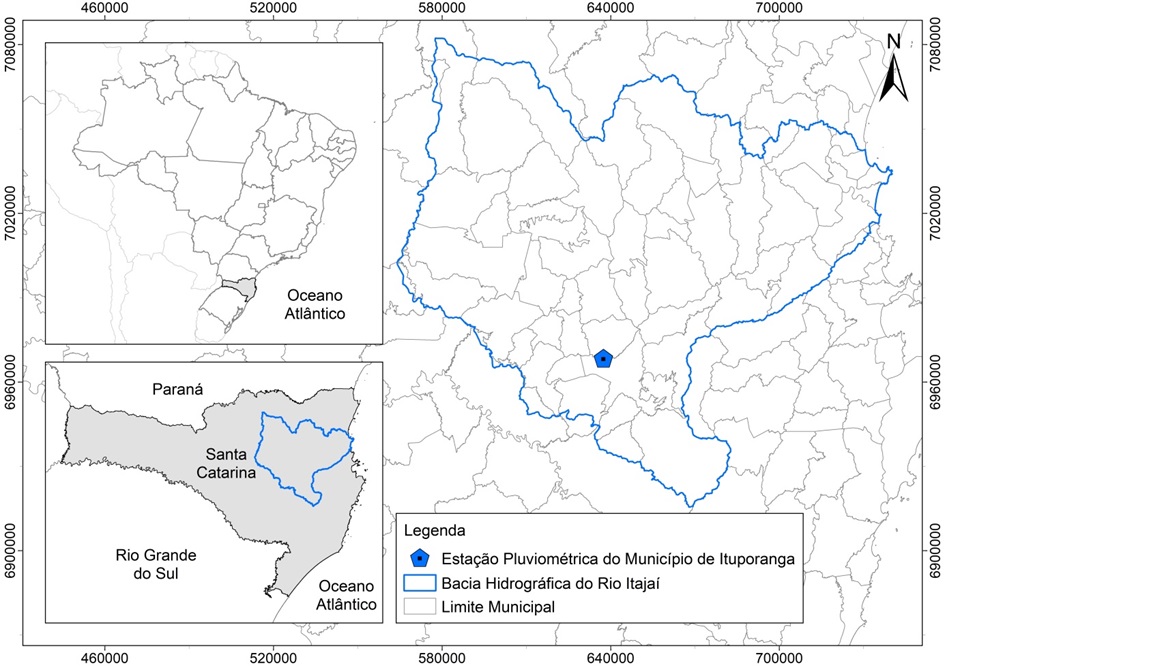
is defined as the aggressiveness of rain as an erosive agent. Estimating rainfall erosivity is important for evaluating soil erosion and planning agricultural activities, management, and conservation practices. To analyze the aggressiveness and erosivity indices of rain in Ituporanga, SC, monthly rainfall data from 1941 to 2021 from the rainfall station of the National Water and Basic Sanitation Agency (ANA), located in Ituporanga, SC were used. The Fournier Index (IF), Modified Fournier Index (IFM), Total Erosivity Index (IET), and the Erosivity Index (EI30) were calculated. The average FI obtained was 18.1, which is classified as low aggressiveness. The IFM was 123, classified as High Aggressiveness. The IET is 1060.39mm, which is classified as
low. The EI30 erosivity index is 7549MJ mm ha−1h−1 year-1, classified as High. The annual rainfall variation determines rainfall erosivity values ranging from 4800 to 13477MJ mm ha−1h−1 year-1.
Metrics
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Epagri - Revista Agropecuária Catarinense
- Publisher
- Empresa de Pesquisa Agropecuária e Extensão Rural de Santa Catarina - Epagri
References
AGÊNCIA NACIONAL DE ÁGUAS E SANEAMENTO BÁSICO - ANA. Hidroweb: Sistemas de Informações Hidrológicas. Disponível em: http:// hidroweb.ana.gov.br. Acesso em: 10 Jan. 2023.
ARNOLDUS, H.M. An approximation of the rainfall factor in the Universal Soil Loss Equation. In: Assessments of Erosion, John Wiley and Sons Ltd, p. 127-132, 1980.
BACK, Á.J. Informações climáticas e hidrológicas dos municípios catarinenses (com programa HidroClimaSC). Florianópolis: Epagri, 2020. 157p.
BACK, Á.J.; GONÇALVES, F.N.; FAN, F.M. Spatial, seasonal, and temporal variations in rainfall aggressiveness in the South of Brazil Engenharia Agrícola, v.39, n.4, p.466-475, 2019.
BACK, Á.J.; POLETO, C. Avaliação temporal do potencial erosivo as chuvas de Florianópolis-SC. Revista Brasileira de Climatologia, v.21, p.264-283, 2017.
BACK, Á.J. ; SÔNEGO, M.; PEREIRA, J.R. Índices de concentração de chuvas na região Sul do Brasil. Revista Brasileira de Climatologia, v.27, p.57-72, 2020.
BAECHELER, J.V.; BRAVO, B.S. Analysis of aggressiveness rainfall in the Far North Of Chile. E-proceedings of the 38th IAHR World Congress September 1-6, 2019, Panama City, Panama.
BALLABIO, C.; BORRELLI, P.; SPINONI, J.; MEUSBURGER, K.; MICHAELIDES, S.; BEGUERÍA, S.; KLIK, A.; PETAN, S.; JANECEK, M.; OLSEN, P.; AALTO, J.; LAKATOS, M.; RYMSZEWICZ, A.; DUMITRESCU, A.; PERCEC, M.; DIODATO, N.; KOSTALOVA, J.; ROUSSEVA, S.; BANASIK, K.; ALEWELL, C.; PANAGOS, P. Mapping monthly rainfall erosivity in Europe. Science of the Total Environment, v.579, p.1298-1315, 2017.
BERTOL, I. Avaliação da erosividade da chuva na localidade de Campos Novos (SC) no período de 1981-1990. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, v.29, p.1453-1458, 1994.
CASTELÁN VEGA, R.; FLORES, V. T.; FLEITES, G.; MONTALVO, A. C. Agresividad de las precipitaciones en la subcuenca del río San Marcos, Puebla, México. Investigaciones Geográficas, Boletín, n.83, p.28-40, 2014.
COMAN, A.M.; LACATUSU, G.; MACSIM, A.M.; LAZAR, G. Assessment of soil erosion using Fournier Indexes to estimate rainfall erosivity. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal, v.18, n.8, p.1739-1745, 2019.
DAVUDIRAD, A.A.; SADEGHI, S.H.; SADODDIN, A. The Impact of development plans on hydrological changes in the Shazand Watershed Iran. Land Degradation & Development, v.27, p.1236-1244, 2016.
DI LENA, B.; ANTENUCCI, F.A.; VERGNI, L.; MARIANI, L. Analysis of the Climatic Aggressiveness of Rainfall in the Abruzzo Region. Italian Journal of Agrometeorology, v.1, p.33-44, 2013.
EMBRAPA. Solos do Estado de Santa Catarina. Rio de Janeiro: Embrapa Solos, 2004. 1384p.
ESCOBAR, G.C.J.; SELUCHI, M.E.; ANDRADE, K. Classificação sinótica de frentes frias associadas a chuvas extremas no Leste de Santa Catarina. Revista Brasileira de Meteorologia, v.31, n.4, p.649-661, 2016
ESSEL, P.; GLOVER, E.T.; YEBOAH, S.; ADJEI-KYEREME, Y.; YAWO, I.N.D.; NYARKU, M.; ASUMADU-SAKYIM, G.S.; GBEDDY, G.K.; AGYRI Y.A.; AMEHO, E. M.; ATULE, E. Rainfall erosivity index for the Ghana Atomic Energy Commission site. Springerplus, v.5, n.465, 2016.
FOURNIER, F. Climat et erosion; la relation entre l’erosion du sol par l’eau et les precipitations atmospheriques. Presses Universitaires de France, Paris, France. 1960.
HAZBAVI, Z.; SADEGHI, S.H.R. Potential effects of vinasse as a soil amendment to control runoff and soil loss. Soil, v.2, p.71-78, 2016.
HLALELE, B.M. Stochastic soil erosion risk modelling and simulation using Fournier Index. Eco. Env. & Cons., v.25, p.S166-S172, 2019.
IBGE - Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Levantamento sistemático da produção agrícola: pesquisa mensal de previsão e acompanhamento das safras agrícolas no ano civil. Rio de Janeiro: IBGE, 2017. 81p.
LIMA, M.T.; OLIVEIRA, C.W.; MOURA-FÉ, M.M. Análise multicritério em geoprocessamento como contribuição ao estudo da vulnerabilidade à erosão no estado do Ceará. Revista Brasileira de Geografia Física, v.14, n.5, p.3156-3172, 2021.
LOSS, A.; BASSO, A.; OLIVEIRA, B.S.; KOUCHER, L. P.;OLIVEIRA, R.A.; KURTZ, C.; LOVATO, P.E.; CURMI, P.; BRUNETTO, G.; COMIN, J.J. Carbono orgânico total e agregação do solo em sistema de plantio direto agroecológico e convencional de cebola. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, v.39, p.1212-1224, 2015
LUKIĆ,T.; LEŠČEŠEN,I.; SAKULSKI D.; BASARIN, B. JORDAAN, A. Rainfall erosivity as an indicator of sliding occurrence along the Southern Slopes of the Bačka Loess Plateau: A case study of the Kula Settlement, Vojvodina (North Serbia). Carpathian Journal of Earth and Environmental Sciences, v.11, n.2, p.303-318, 2016.
OLIVER, J.E. Monthly precipitation distribution: A comparative index. The Professional Geographer, v.32, n.3, p.300-309, 1980.
PATRICHE, C.V.; ROS, CA, B.; PÎRN˘AU, R.G.; VASILINIUC, I.; IRIMIA, L.M. Simulation of Rainfall Erosivity Dynamics in Romania under Climate Change Scenarios. Sustainability, v.15, n.2, 1469, 2023. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021469
PINTO DOS SANTOS, V.; BERTOL, I. SANTOS, A.P.; KURTZ, C.; WOLSCHICK, N.H.; BAGGIO, B.; WROBLESCKI, F.A.; PRAZERES, M.S. Erosão hídrica no cultivo da cebola influenciada pelo manejo do solo e cobertura por resíduo cultural. Ciência del Suelo, v.40, n.2, p.185-195, 2002.
RAMIREZ-ORTIZ, F.A.; HINCAAPIÉ-GOMEZ, E.; SADEGHIAN-KHALAJABADI, S.; PEREZ-GOMEZ, U. Erosividad de las lluvias en la Zona Cafetera Central y Occidental del Departamento de Caldas. Cenicafé, v.58, n.1, p.40-52, 2007.
RENARD, K.G.; FOSTE, G.R.; WEESIES, G.A.; McCOOL, D.K; YODER, D.C. Predicting soil erosion by water: a guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agriculture Handbook No. 703, 404 pp. 1997.
SADEGHI, S.H., ZABIHI, M., VAFAKHAH, M.; HAZBAVI, Z. Spatiotemporal mapping of rainfall erosivity index for different return periods in Iran. Natural Hazards, v.87, n.1, p.35-56, 2017.
TSITSAGI, M.; BERDZENISHVILI, A.; GUGESHASHVILI, M. Spatial and temporal variations of rainfall-runoff erosivity (r) factor in Kakheti, Georgia. Annals of Agrarian Science, v.16, n.2, p.226-235, 2018.
TUCCI, C.E.M. Hidrologia: Ciência e aplicação. Porto Alegre. Ed. Universidade/UFRGS, 2015. 943p.
VELASCO, I.; CORTÉS, G. Índices de Fournier modificado y de concentración de la precipitación, como estimadores del factor de riesgo de la erosión, en Sinaloa, México. Avances en estudios sobre desertificación: aportaciones al Congreso Internacional sobre Desertificación, 1, 2009. Anais[…]. Murcia, Espanha. p.431-434
WISCHMEIER, W.H., SMITH, D.D. Predicting rainfall erosion losses: a guide to conservation planning. U.S Department of Agriculture, Agr. Handbook, 537:1-58, 1978.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Alvaro Jose Back Back, Juliane Garcia Knapik Justen, Clístenes Antônio Guadagnin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




