Effects of temperature and humidity on the development and food consumption of Bombyx mori in Syrgaria in Mato Grosso do Sul
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.52945/rac.v38i3.2210Keywords:
Silkworm, Environmental conditions, sericulture, bioecologyAbstract
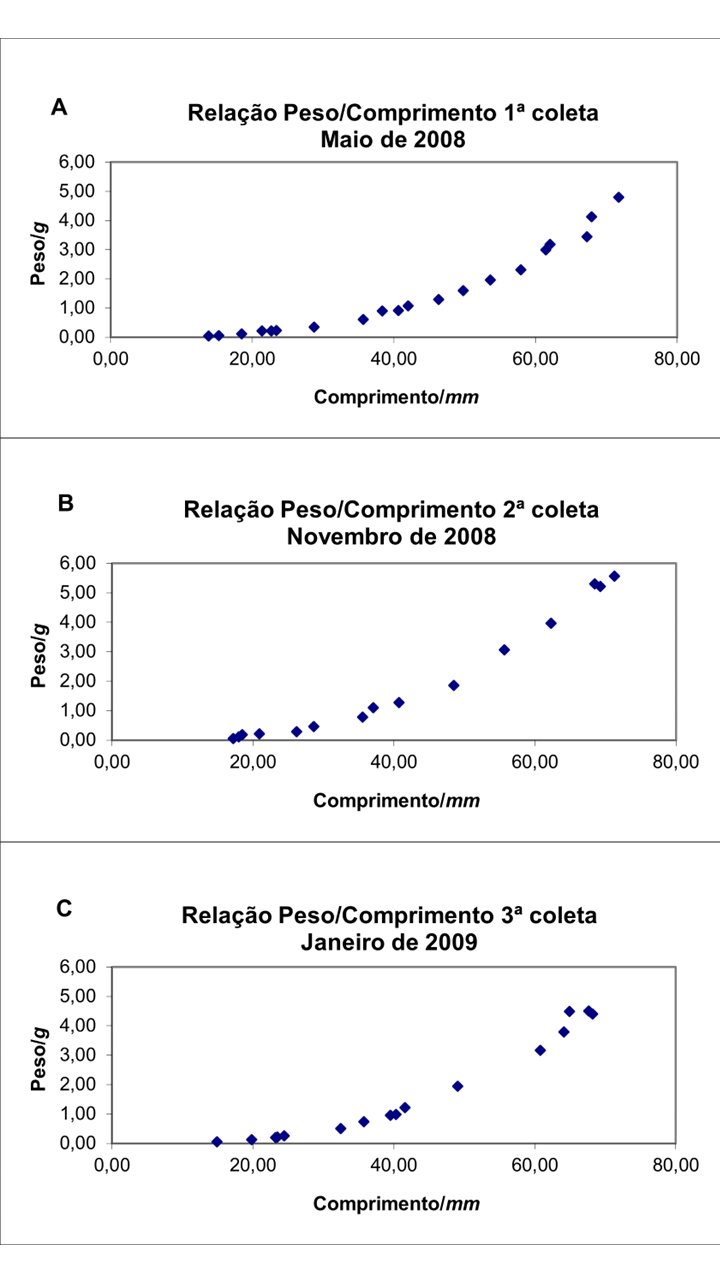
Sericulture involves raising silkworms for the production of silk. Brazil is the seventh-largest silk producer, employing small family farmers. Considering that climate change has drastically altered production environments in recent years, the objective of this study was to evaluate the influence of temperature and humidity on the development of Bombyx mori L. throughout the seasons (fall, spring and summer). The experiment was conducted at the Indaiá Settlement in the municipality of Itaquiraí, Mato Grosso do Sul, from May to November 2008 and January 2009. The mulberry cultivar used was Korin, and temperature and relative humidity data in the sheds were monitored with a thermohygrometer. The method used to quantify the silkworm's nutritional diet was based on three measurements: the weight of food consumed, the weight of feces, and the weight gained by the insect. No influence of temperature and humidity on biometric and nutritional parameters was observed. The results indicate that the continuous supply of food exerted a greater influence on larval development than variai-os in temperature and humidity.
Downloads
References
BORTOLI, S. A.; MONTAGNA, M. A.; MIRANDA, J. E.; MURATA, A. T.; TAKAHASHI, R. Índices de consumo e utilização de cultivares de amoreira por Bombyx mori L. Revista de Agricultura, Piracicaba, v. 77, n. 1, p. 65-77, 2002. DOI: https://doi.org/10.37856/bja.v77i1.1343.
FAOSTAT. Found and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 2025. Disponível em: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL/visualize. Acesso em: 28 outubro 2025.
KHAN, M. M. Effects of Temperature and R. H. % on Commercial Characters of Silkworm (Bombyx mori L.) cocoons in Anantapuramu district of AP, India. Research Journal Agricultural Forest Science, v. 2, n. 11, p. 1-3, 2014. Disponível em: https://www.isca.in/AGRI_FORESTRY/Archive/v2/i11/1.ISCA-RJAFS-2014-034.php. Acesso em: 25 agosto 2025.
LOPES, T. B. F.; RACHEL, C. M. A.; SOUZA, R. F.; NASCIMENTO, C. C.; DIONÍSIO, J. F.; MANTOVANI, M. S.; SEMPREBON, S. C.; ROSA, R. DA. Influence of temperature variation on gene expression and cocoon production in Bombyx mori Linnaeus, 1758 (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology - Part D: Genomics and Proteomics, v. 47, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbd.2023.101111
MARCHI, S.; FODRA, R. C.; MARCHI, L.; PEREIRA, L. H.; SANTANA, D. F.; SIGNORINI, T.; RUIZ, H. B.; OLIVEIRA, J. R. DE; FERREIRA, G. A. Influência da alimentação na morfologia da glândula sericígena de lagartas no 5º instar de Bombyx mori L. utilizando diferentes cultivares de amoreira. Arquivos Ciências Veterinárias e Zoologia, v. 12, n. 1, p. 17-22, 2009. Disponível em: https://revistas.unipar.br/index.php/veterinaria/article/view/2929. Acesso em: 25 agosto 2025.
PANUCCI-FILHO, L.; CHIAU, A. V.; PACHECO, V. O custo da Sericicultura: A produção de casulos de bicho-da-seda no Paraná. Revista em Agronegócios e Meio Ambiente, v. 4, n. 1, p. 37-55, 2011. Disponível em: https://periodicos.unicesumar.edu.br/index.php/rama/article/download/1747/1185. Acesso em: 25 agosto 2025.
PINTO, N. F.; MUROFUSE, N. T.; CARVALHO, M. de. Processo e cargas de trabalho e a saúde dos trabalhadores na sericicultura: uma revisão. Revista Brasileira de Saúde Ocupacional, v. 40, n. 132, p. 237-247, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/0303-7657000095514.
PORTO, A. J.; FUNARI, S. R. C.; DIERCKX, S. M. A. G. Consumo e utilização do alimento pelo Bicho-da-Seda (Bombyx mori L.), alimentado com dois cultivares de amoreira em diferentes idades de corte. Ciência Animal Brasileira, v. 7, n. 2, p. 153-166, 2006. Disponível em: https://revistas.ufg.br/vet/article/view/399/374. Acesso em: 25 agosto 2025.
PORTO, A. J.; OKAMOTO, F.; CUNHA, E. A.; OTSUK, I. P. Caracterização de oito raças do bicho da seda (Bombyx mori L.). Ciência Rural, v. 34, n. 1 p. 259-264, 2004. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-84782004000100040
RABHA, M.; ETHUNGBENI, T. N.; RAHUL, K.; ALAM, K.; MAHESWARI, M. Temporal analysis of climatic factors influencing silkworm disease incidences in commercial sericulture crops of West Bengal, India (2018–2024). The Journal of Basic and Applied Zoology, v. 86, p. 65-72, 2025. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41936-025-00483-0
SABBAG, O. J.; NICODEMO, S.; OLIVEIRA, J. E. M. Custos e viabilidade econômica da produção de casulos do bicho-da-seda. Pesquisa Agropecuária Tropical, v. 43, n. 2, p. 187-194, 2013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1983-40632013000200004
SUJATHA, G. S.; KUMAR, G. A.; TEJA, K. S. S.; DEVI, D. L.; MADHURI, V.; PANDA, A.; RUPALI R. J. S.; GAUTAM, S. K. 2024. “A Comprehensive Review of the Effect and Mitigation of Climate Change on Sericulture”. International Journal of Environment and Climate Change, v. 14, n. 7, p. 776–788, 2024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.9734/ijecc/2024/v14i74317.
WALDBAUER, G. P. The consumption and utilization of food by insect. Advances in Insect Physiology, v. 5, p. 229-282, 1968. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2806(08)60230-1
WANG, Y.; ZHANG, X. ; TIAN, C.; GUO, X.; SHU, Q.; GU, H.; FENG, P.; LI, F.; BING LI, B. Effects of different diets on thermal tolerance in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Entomologia Experimentallis et Applicata, v. 172, n. 1, p. 27-34, 2023 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/eea.13382
ZAMBRANO-GONZÁLEZ, G.; ALMANZA, M.; VÉLEZ, M.; RUIZ-ERAZO, X. Effect of environmental conditions on the changes of voltinism in three lines of Bombyx mori. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências, v. 95, n. 1, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765202320210122
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Édiston Tomazelli, Dr. Marcos Massuo Kashiwaqui, Dra. Adriane da Fonseca Duarte, Dra. Elaine Antoniassi Luiz Kashiwaqui

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 (CC BY 4.0 - internacional), permite:
Compartilhar — copiar e redistribuir o material em qualquer meio ou formato para qualquer finalidade, mesmo comercialmente.
Adaptar — remixar, transformar e desenvolver o material para qualquer propósito, mesmo comercialmente.





